Chapter 06 - Getting User Data
The main goal of an application is to process data. This data can be requested from the user, read from a file, retrieved from the Internet, be randomly generated, ...
Requesting User Input
If requesting input from the application user, the application can be made more user-friendly and dynamic.
Requesting user input is not that hard. All one has to do is output a message to the user stating what is expected if him/her and allow the user to input the actual data.
Basically when a user enters something via the terminal, it is considered to be a string. If we wish to approach the data as an integer or another type of value, it needs to be parsed (converted). C# makes this really simple by providing some methods to convert these strings to integral of floating-point numbers.
Requesting a String
Requesting a piece of text from the user is very simple. While the Console.WriteLine() method provides a way to easily write a string to the terminal, the method Console.ReadLine() does the opposite. It lets the user input a string which can then be programmatically be stored in a variable of type string.
The following code snippet requests the user to input his/her name. Next the input is used to output a personalized greeting to the user.
Console.Write("Please enter your name: ");
string name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + name + ". Very nice to meet you.");
Output
Please enter your name: Nico
Hello Nico. Very nice to meet you.
Some remarks are needed about this code example:
- Instead of
Console.WriteLine()the snippet makes use ofConsole.Write(), allowing the user to type after the question. Nothing wrong ifConsole.WriteLine()would of been used, it just feels more natural this way. - The variable
nameis declared when needed, not beforehand. Some people that come from the world of C-programming may have the habit to declare all variables at the top ofMain(), but this is not needed and even discouraged. - The method
Console.ReadLine()is called and it returns a result (a string with the text that the user typed). By assigning the result to the variablenameof the typestring, it can be used later in the code.
Requesting an Integer
When requesting an other type of data from the user, the input first needs to be parsed to the correct data type. C# cannot know from itself what kind of data the user provided.
Below is a code snippet that shows how to use the Convert class to parse the input from the user as an integer by using the ToInt32() method to parse the provided string as an integer.
Console.Write("Please enter your age: ");
string ageText = Console.ReadLine();
int age = Convert.ToInt32(ageText);
Console.WriteLine("How interesting that you are " + age + " years young.");
Output
Please enter your age: 33
How interesting that you are 33 years young.
Take note on how the ageText variable is passed to the ToInt32() method. Again the ToInt32() method returns a resulting value. If we wish to save this for later processing, it needs to be stored in a variable (age in this case).
This example can actually be written a bit more compact. The value that is returned by the Console.ReadLine() can actually be passed to the Convert.ToInt32() method directly. This makes the code shorter and it is perfectly possible as the string value is not required anymore after the conversion.
Console.Write("Please enter your age: ");
int age = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("How interesting that you are " + age + " years young.");
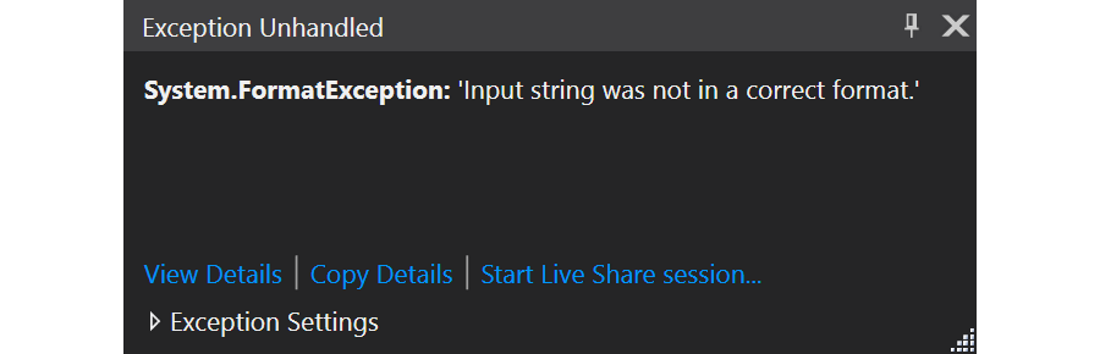
⚡ FormatException
Do note that when entering an invalid number such as a or 123.23 will cause the application to crash with a FormatException. Feel free to test this. For the moment, fixing this is too complex. This course will return to this later.
Make sure you understand the previous code example before continuing. If not, read it a couple of times or execute it in debug in Visual Studio.
Requesting a Double
Requesting floating-point numbers from the user is very similar to requesting integral values. Instead of using the ToInt32() method of Convert, one can use the ToDouble() method of Convert.
Console.Write("Please enter your height in meters: ");
double height = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("You are quite tall with a height of " + height + "m.");
Output
Please enter your height in meters: 1.86
You are quite tall with a height of 1.86m.
Generating Random Numbers
An other approach to get data is to generate it randomly. The Random class of C# also provides the tools to generate all sorts of random numbers.
The code snippet belows contains the necessary code to generate integral numbers between a minimum value (inclusive) and the provided maximum (exclusive) bound. If you only provide a single number it will take this as the exclusive maximum and provide a number between 0 and this maximum.
// Object of the Random class that allows us to
// generate numbers
Random generator = new Random();
// [1, 7[
int die = generator.Next(1, 7); // Value 1 to 6
// [0, 12[
int month = generator.Next(0, 12); // Value 0 to 11
// [0, 21[
int examScore = generator.Next(21); // Value 0 to 20
Don't worry too much about the new keyword and such just yet.
Floating Point Values
The Random class can also generate random floating point values between 0.0 and 1.0. This can be achieved by calling the NextDouble() method. No upper limit can be provided here. You need to do this yourself.
// Object of the Random class that allows us to
// generate numbers
Random generator = new Random();
// [0.0, 1.0[
double real = generator.NextDouble();
